Hearing Aids: Styles, Costs, and Features Explained
Hearing Aid Styles: Behind-the-Ear vs. In-the-Ear
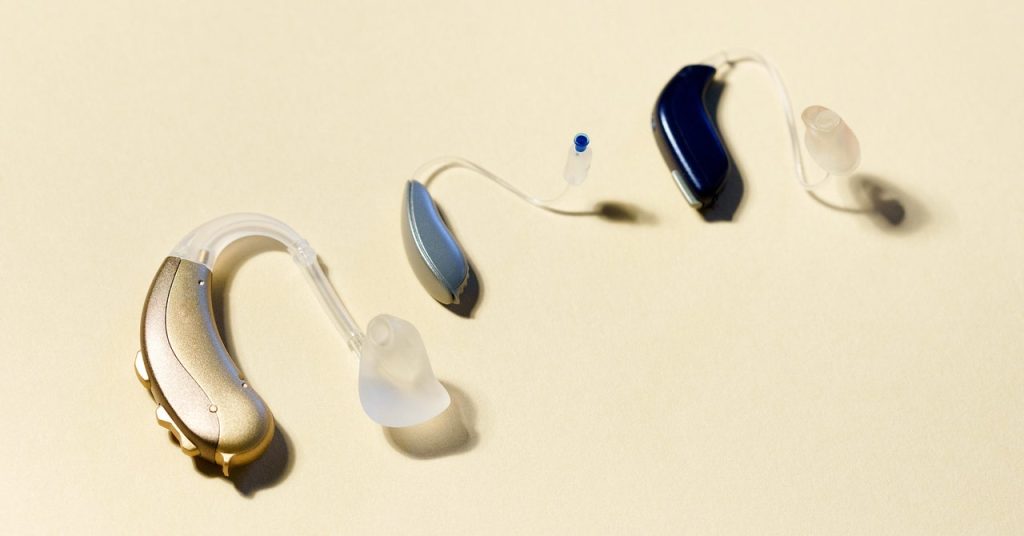
When it comes to hearing aids, consumers have two primary options: behind-the-ear (BTE) and in-the-ear (ITE) styles. BTE hearing aids feature a plastic case that sits behind the ear, housing the device’s electronics, including the amplifier and microphone. A thin cable runs over the top of the ear and into the ear canal, connecting to a tiny speaker called a receiver, which delivers the amplified sound. While modern BTE hearing aids are more compact and discreet than their predecessors, their distinctive design still makes it apparent that the wearer is using a hearing aid. Additionally, properly positioning BTE aids can be challenging, especially for those who wear glasses.
In contrast, ITE hearing aids are self-contained units that often resemble Bluetooth earbuds. These devices integrate all the necessary electronics into a single unit that fits inside the ear. Although not entirely invisible, ITE aids avoid the dated appearance associated with BTE models. However, wearing earbuds in social situations may not be considered the best etiquette. ITE aids are easier to insert and remove, making them a convenient choice for those who prefer to wear hearing aids intermittently throughout the day.
The Cost of Hearing Aids
Prior to the availability of over-the-counter hearing aids, units typically cost between $1,000 and $6,000, with most people spending around $4,600 for a pair. The high cost was primarily due to the bundling of the devices with services from audiologists or other hearing professionals. These services often included hearing tests, fittings, and ongoing adjustments to ensure optimal performance.
Rechargeable vs. Disposable Batteries
Many modern hearing aids feature rechargeable batteries, providing a convenient and eco-friendly solution. Rechargeable hearing aids can last for 12 to 30 hours on a single charge, depending on factors such as streaming audio and noise cancellation. Charging times vary, with some models reaching a full charge within three hours, while others may take up to six hours.
Some hearing aids still use disposable batteries, particularly those with smaller sizes. While dealing with tiny batteries can be challenging, they offer the advantage of lasting up to 70 hours or more, surpassing even the best rechargeable models.
Bluetooth Connectivity and Audio Streaming
Many modern hearing aids offer Bluetooth connectivity, allowing users to stream audio directly from smartphones, tablets, or televisions. This feature enables wearers to enjoy music, podcasts, or phone calls without the need for additional devices. Some hearing aids also provide remote control functionality through companion smartphone apps, making it easy to adjust settings and volume on the go.
Noise Reduction and Directionality
Advanced hearing aids often incorporate noise reduction and directional microphone technology to enhance the listening experience in challenging environments. Noise reduction algorithms analyze and filter out background noise, while directional microphones focus on sound coming from specific directions, such as the person speaking in front of the wearer. These features can significantly improve speech understanding and overall comfort in noisy situations.
3 Comments
Good to know, but does it explain why they cost as much as a small car?
Finally, a guide that makes sense of the maze that is hearing aid shopping!
Aria Turner: Finally, something that doesn’t just amplify the confusion!